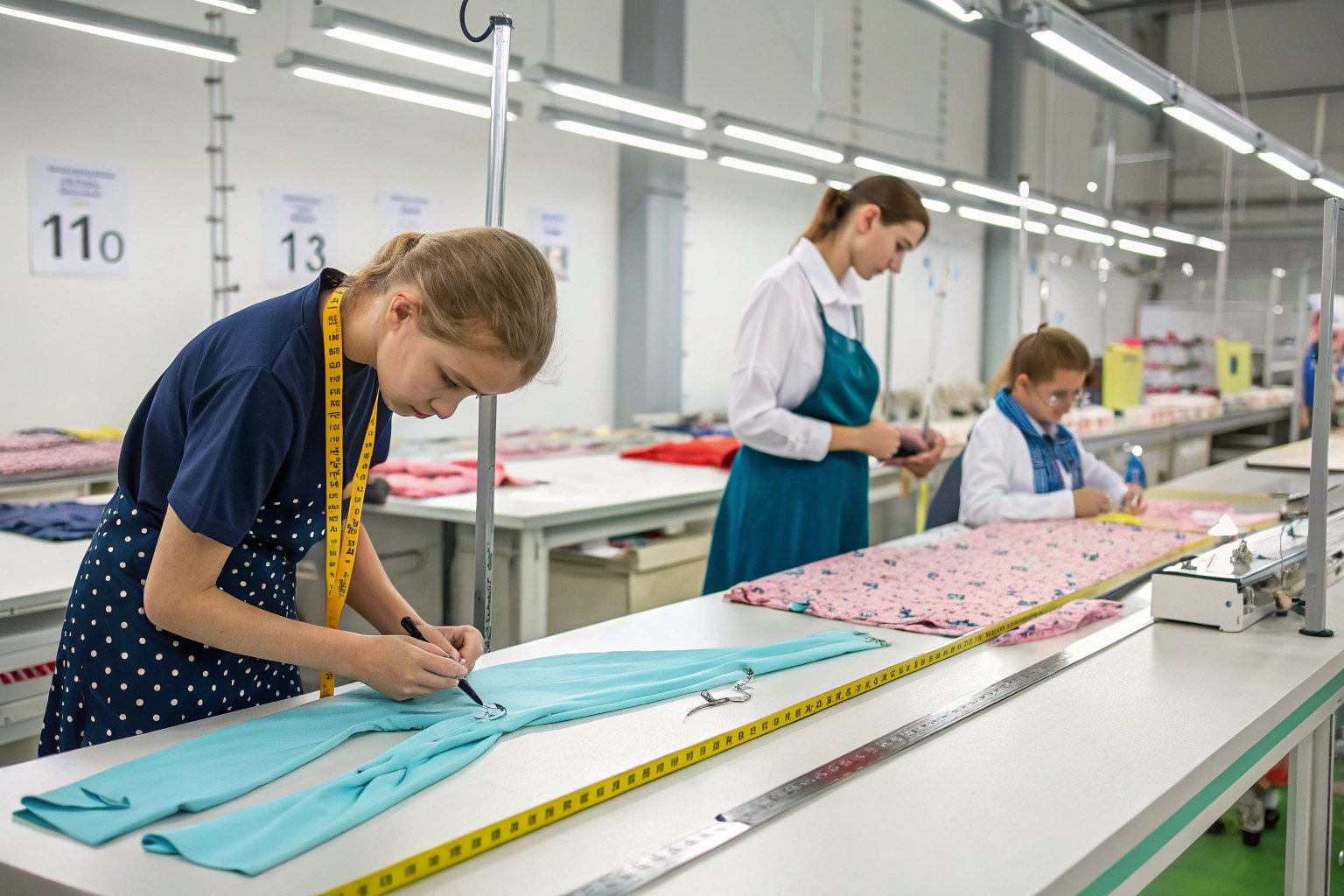
Quality control in children's clothing production requires heightened vigilance due to the unique safety requirements, sensitive wearers, and discerning parents who expect exceptional standards. As a manufacturer specializing in children's apparel, I've developed comprehensive quality systems that address both conventional quality metrics and child-specific safety considerations that differentiate kids wear from adult clothing.
Effective quality control for kids clothing requires implementing rigorous inspection protocols at multiple production stages, focusing on safety compliance, fabric integrity, construction durability, and chemical safety. This involves establishing clear quality standards, training specialized inspectors, utilizing appropriate testing equipment, and maintaining detailed documentation throughout the production process.
Managing quality in children's apparel demands a systematic approach that begins with raw material selection and continues through final packaging. Let's explore the key components of a robust quality management system for kids clothing production.
What are the critical inspection points in production?
Establishing strategic inspection points throughout the production process enables early problem detection and prevents quality issues from progressing to subsequent stages. For children's clothing, these checkpoints must address both conventional quality concerns and child-specific safety considerations.
The most critical inspection points include raw material receiving, cutting verification, during production checks, and final random inspection. Each stage serves a distinct purpose in the quality assurance process, with specific tests and acceptance criteria tailored to children's wear requirements.

Why is fabric inspection so crucial for kids wear?
Fabric inspection is crucial because materials represent the foundation of garment quality and safety, with children's specific vulnerabilities requiring extra vigilance. Before cutting, fabrics must be checked for defects like shading variations, knitting flaws, printing errors, and consistency issues that might affect the final product. According to ASTM textile standards, children's fabrics require additional testing for colorfastness, pilling resistance, and dimensional stability beyond standard apparel requirements. Additionally, verification of safety certifications like Oeko-Tex Standard 100 must occur at this stage, as fabric-related safety issues cannot be rectified later in production. Proper fabric inspection prevents the waste of cutting and sewing resources on substandard materials.
What during-production checks prevent final defects?
During-production checks identify issues while manufacturing is still underway, allowing for immediate correction before problems multiply. These inline inspections include verifying pattern matching, checking seam consistency, ensuring accurate stitch density, and confirming proper application of trims and embellishments. For children's wear specifically, inspectors must verify that safety features like secure snap fasteners, properly stitched elastic, and reinforced stress points meet specifications. The most effective during-production quality control implements a first article inspection system where the first completed garment from each production lot undergoes comprehensive checking before mass production continues. This approach catches issues early when correction is most cost-effective.
How to implement effective safety compliance checks?
Safety compliance represents the non-negotiable foundation of children's wear quality control, with stringent regulations governing multiple aspects of production. Effective compliance checking requires specialized knowledge of applicable standards and systematic verification processes.
Key safety compliance areas include small parts testing, flammability requirements, chemical restrictions, and physical mechanical hazards. Each category demands specific testing protocols and documentation to ensure regulatory adherence and child safety.

What small parts testing prevents choking hazards?
Small parts testing prevents choking hazards by verifying that components cannot detach and pose risks to young children who explore objects with their mouths. This testing involves applying specific force to buttons, snaps, appliqués, and other decorative elements using calibrated pull test equipment that simulates the strength a child might exert. According to CPSC guidelines, any component of children's clothing for ages 3 and under must withstand a 15-pound pull force, while items for children 3-6 years must withstand 10 pounds. Additionally, functional components like drawstrings have length restrictions and attachment requirements that vary by garment type and child's age. Proper small parts testing requires both initial component verification and periodic production checks to ensure consistency.
How does flammability testing protect children?
Flammability testing protects children by ensuring sleepwear and certain other garments meet strict fire resistance standards that reduce burn injury risks. The CPSC flammability standards for children's sleepwear require specific testing protocols where fabric samples are exposed to vertical flame sources under controlled conditions. To pass, fabrics must self-extinguish quickly and have limited char length. These requirements differ for sizes 0-6X versus 7-14, and vary between tight-fitting versus loose garments. Compliance typically involves either using inherently flame-resistant fabrics or treating materials with flame retardants—though the latter approach requires additional chemical safety verification. Proper flammability testing includes both fabric certification upon receipt and random production testing to ensure treated fabrics maintain their protective properties through manufacturing processes.
What quality standards apply specifically to children's wear?
Children's clothing must adhere to numerous specialized quality standards that address their unique usage patterns, safety requirements, and durability expectations. Understanding these standards is essential for establishing appropriate quality benchmarks.
Key children's-specific standards include reinforced construction requirements, stricter size tolerances, enhanced durability testing, and specialized care labeling. The table below outlines critical quality differentiators between children's and adult apparel:
| Quality Aspect | Children's Wear Requirements | Adult Wear Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Seam Strength | Higher stress requirements for active use | Standard strength requirements |
| Size Tolerance | Tighter tolerances for proper fit | Broader acceptable ranges |
| Durability | Enhanced testing for repeated washing | Standard durability expectations |
| Safety Features | Multiple child-specific requirements | Basic safety considerations |
Why do construction standards differ for children's clothing?
Construction standards differ for children's clothing because garments undergo more strenuous use, frequent washing, and must accommodate active movement and growth. Seams require reinforcement at stress points like knees, seats, and armholes that experience extra strain during play. According to industry construction guidelines, children's wear typically specifies higher stitches per inch (SPI) for major seams—often 12-16 SPI compared to 8-12 for adult clothing—to prevent seam failure during active use. Additionally, techniques like bar-tacking at stress points, reinforced crotch seams, and secure elastic application are standard requirements rather than premium features in quality children's wear. These enhanced construction standards ensure garments withstand the rigors of childhood activities while maintaining appearance through numerous wash cycles.
How do size and fit tolerances ensure quality?
Size and fit tolerances ensure quality by maintaining consistency across production runs and guaranteeing garments match labeled size expectations. Children's wear typically employs tighter tolerances than adult clothing—often ±¼ inch instead of ±½ inch—because proper fit is more critical for both comfort and safety. According to AAFA size specification guidelines, children's clothing must account for both current fit and growth accommodation, requiring precise execution of intended ease. Additionally, proportional consistency across different size ranges is crucial, as parents often purchase multiple sizes for growing children and expect consistent fit relationships. Proper size quality control involves regular measurement verification using standardized methods and equipment, with statistical process control to identify trending deviations before they become quality issues.
How to establish comprehensive testing protocols?
Comprehensive testing protocols provide objective data to support quality decisions and ensure consistent adherence to standards. Effective testing encompasses physical, chemical, and performance evaluations throughout the production process.
Key testing categories include fabric performance, colorfastness, construction integrity, and chemical safety. Each requires specific equipment, methodologies, and acceptance criteria tailored to children's wear requirements.

What performance tests verify durability?
Performance tests verify durability by simulating the conditions garments will encounter during use and care, identifying potential failure points before products reach consumers. Standard durability testing includes Martindale abrasion resistance tests for fabric surface wear, multi-directional stretch and recovery tests for knit garments, and seam slippage tests that measure stitch integrity under stress. For children's wear specifically, additional testing might include repeated closure operation (zippers, snaps, buttons) to ensure they withstand frequent use, and color transfer tests for printed areas that might contact skin or other garments during active play. These performance tests should be conducted on both initial production samples and periodically throughout manufacturing to ensure consistent quality.
How does colorfastness testing ensure safety?
Colorfastness testing ensures safety by verifying that dyes and prints remain stable and don't transfer to skin or other surfaces, potentially causing irritation or contamination. The ISO 105 colorfastness standards provide testing methodologies for various conditions including perspiration, rubbing, washing, and light exposure. For children's wear, perspiration and saliva colorfastness are particularly important since children may chew on their clothing or experience heavy sweating during activity. Additionally, testing for color migration to ensure prints and dyes don't transfer to skin addresses both aesthetic concerns and potential chemical exposure risks. Proper colorfastness verification includes testing all color variations within a collection, as different dyes may behave differently even on identical fabrics.
How to document and improve quality systems?
Documentation provides the foundation for consistent quality management and continuous improvement. Well-designed quality systems generate data that identifies trends, pinpoints recurring issues, and measures improvement over time.
Effective quality documentation includes inspection reports, test records, corrective action documentation, and supplier performance tracking. These records create accountability and provide insights for systematic quality enhancement.

What quality metrics provide meaningful insights?
Quality metrics provide meaningful insights when they track both outcome measures and process indicators that predict final quality. Key performance indicators for children's wear quality include first-pass yield rates, defect rates by category, return rates for quality issues, and customer complaint patterns. According to quality management principles, the most effective metrics are specific, measurable, actionable, relevant, and timely (SMART). For children's wear, additional metrics might track safety compliance rates, size consistency measurements, and performance test results over time. These metrics should be reviewed regularly to identify trends, with root cause analysis conducted for any metric falling outside established control limits.
How can supplier collaboration enhance quality?
Supplier collaboration enhances quality by creating partnerships focused on prevention rather than detection of issues. This approach involves sharing quality data with material suppliers, conducting joint problem-solving sessions, and establishing mutual quality objectives. The most effective collaborations include supplier quality agreements that clearly define expectations, testing responsibilities, and communication protocols. For children's wear specifically, suppliers should understand the unique safety requirements and be involved in material selection decisions that affect final product quality. Regular supplier performance reviews, combined with technical support for quality improvement initiatives, create relationships where both parties are invested in achieving excellence rather than simply meeting minimum requirements.
Conclusion
Managing quality control for kids clothing production requires a comprehensive, systematic approach that addresses both conventional quality metrics and child-specific safety considerations. From raw material inspection through final packaging, each production stage demands specific checks and documentation to ensure consistent excellence.
The most successful quality systems combine rigorous inspection protocols with continuous improvement processes that leverage data to prevent issues before they occur. If you're developing children's apparel and need manufacturing partnership with robust quality systems, contact our Business Director Elaine at elaine@fumaoclothing.com. Let Shanghai Fumao's expertise in children's wear quality control help you produce garments that meet the highest standards of safety, durability, and customer satisfaction.









